
The evolution of the trendy graphics processor begins with the primary 3D add-in playing cards in 1995, adopted by the widespread adoption of 32-bit working programs and the inexpensive private pc.
The graphics trade that existed earlier than that largely consisted of a extra prosaic 2D, non-PC structure, with graphics boards higher identified by their chip’s alphanumeric naming conventions and their enormous value tags. 3D gaming and virtualization PC graphics finally coalesced from sources as numerous as arcade and console gaming, army, robotics and area simulators, in addition to medical imaging.
The early days of 3D shopper graphics have been a Wild West of competing concepts. From easy methods to implement the {hardware}, to the usage of completely different rendering methods and their utility and knowledge interfaces, in addition to the persistent naming hyperbole. The early graphics programs featured a set operate pipeline (FFP), and an structure following a really inflexible processing path using nearly as many graphics APIs as there have been 3D chip makers.
While 3D graphics turned a reasonably boring PC trade into a light-weight and magic present, they owe their existence to generations of revolutionary endeavor. This is the primary installment of a TechSpot particular function collection that takes an intensive have a look at the historical past of the GPU. From the early days of 3D shopper graphics, revisiting the game-changer that was 3Dfx Voodoo graphics, and the trade’s consolidation on the flip of the century. Lastly, at the moment’s trendy basic goal GPU that we have come to like…
1976 – 1995: The Early Days of 3D Consumer Graphics
The first true 3D graphics began with early show controllers, generally known as video shifters and video tackle mills. They acted as a pass-through between the primary processor and the show. The incoming knowledge stream was transformed into serial bitmapped video output akin to luminance, colour, in addition to vertical and horizontal composite sync, which saved the road of pixels in a show era and synchronized every successive line together with the blanking interval (the time between ending one scan line and beginning the following).
A flurry of designs arrived within the latter half of the Nineteen Seventies, laying the inspiration for 3D graphics as we all know them. RCA’s “Pixie” video chip (CDP1861) in 1976, as an illustration, was able to outputting a NTSC appropriate video sign at 62×128 decision, or 64×32 for the ill-fated RCA Studio II console.
The video chip was shortly adopted a yr later by the Television Interface Adapter (TIA) 1A, which was built-in into the Atari 2600 for producing the display show, sound results, and studying enter controllers. Development of the TIA was led by Jay Miner, who additionally led the design of the customized chips for the Commodore Amiga pc in a while.

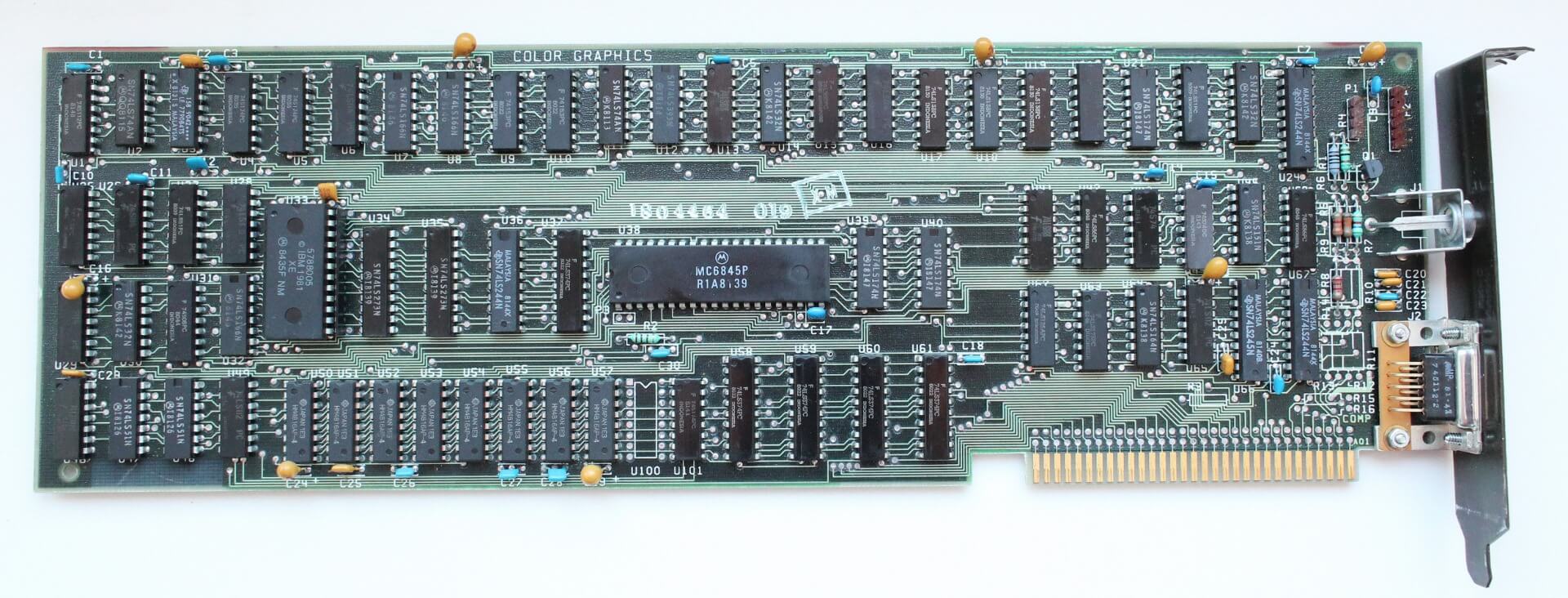
In 1978, Motorola unveiled the MC6845 video tackle generator. This grew to become the premise for the IBM PC’s Monochrome and Color Display Adapter (MDA/CDA) playing cards of 1981, and supplied the identical performance for the Apple II. Motorola added the MC6847 video show generator later the identical yr, which made its manner into numerous first era private computer systems, together with the Tandy TRS-80.
The same resolution from Commodore’s MOS Tech subsidiary, the VIC, supplied graphics output for 1980-83 classic Commodore house computer systems.
In November the next yr, LSI’s ANTIC (Alphanumeric Television Interface Controller) and CTIA/GTIA co-processor (Color or Graphics Television Interface Adaptor), debuted within the Atari 400. ANTIC processed 2D show directions utilizing direct reminiscence entry (DMA). Like most video co-processors, it might generate playfield graphics (background, title screens, scoring show), whereas the CTIA generated colours and moveable objects. Yamaha and Texas Instruments provided comparable IC’s to quite a lot of early house pc distributors.
The subsequent steps within the graphics evolution have been primarily within the skilled fields.
Intel used their 82720 graphics chip as the premise for the $1000 iSBX 275 Video Graphics Controller Multimode Board. It was able to displaying eight colour knowledge at a decision of 256×256 (or monochrome at 512×512). Its 32KB of show reminiscence was enough to attract traces, arcs, circles, rectangles and character bitmaps. The chip additionally had provision for zooming, display partitioning and scrolling.
SGI shortly adopted up with their IRIS Graphics for workstations — a GR1.x graphics board with provision for separate add-in (daughter) boards for colour choices, geometry, Z-buffer and Overlay/Underlay.
Intel’s $1,000 iSBX 275 Video Graphics Controller Multimode Board was able to displaying eight colour knowledge at a decision of 256×256 (or monochrome at 512×512).
Industrial and army 3D virtualization was comparatively nicely developed on the time. IBM, General Electric and Martin Marietta (who have been to purchase GE’s aerospace division in 1992), together with a slew of army contractors, know-how institutes and NASA ran varied initiatives that required the know-how for army and area simulations. The Navy additionally developed a flight simulator utilizing 3D virtualization from MIT’s Whirlwind pc in 1951.
Besides defence contractors there have been corporations that straddled army markets with skilled graphics.
Evans & Sutherland – who have been to offer skilled graphics card collection such because the Freedom and REALimage – additionally supplied graphics for the CT5 flight simulator, a $20 million package deal pushed by a DEC PDP-11 mainframe. Ivan Sutherland, the corporate’s co-founder, developed a pc program in 1961 referred to as Sketchpad, which allowed drawing geometric shapes and displaying on a CRT in real-time utilizing a light-weight pen.
This was the progenitor of the trendy Graphical User Interface (GUI).
In the much less esoteric discipline of non-public computing, Chips and Technologies’ 82C43x collection of EGA (Extended Graphics Adapter), supplied a lot wanted competitors to IBM’s adapters, and might be discovered put in in lots of PC/AT clones round 1985. The yr was noteworthy for the Commodore Amiga as nicely, which shipped with the OCS chipset. The chipset comprised of three essential part chips — Agnus, Denise, and Paula — which allowed a specific amount of graphics and audio calculation to be non-CPU dependent.
In August of 1985, three Hong Kong immigrants, Kwok Yuan Ho, Lee Lau and Benny Lau, fashioned Array Technology Inc in Canada. By the top of the yr, the identify had modified to ATI Technologies Inc.
ATI bought their first product out the next yr, the OEM Color Emulation Card. It was used for outputting monochrome inexperienced, amber or white phosphor textual content in opposition to a black background to a TTL monitor through a 9-pin DE-9 connector. The card got here outfitted with a minimal of 16KB of reminiscence and was accountable for a big share of ATI’s CAD$10 million in gross sales within the firm’s first yr of operation. This was largely performed by way of a contract that provided round 7000 chips every week to Commodore Computers.
ATI’s Color Emulation Card got here with a minimal 16KB of reminiscence and was accountable for a big a part of the corporate’s CAD$10 million in gross sales the primary yr of operation.
The introduction of colour displays and the shortage of an ordinary among the many array of opponents finally led to the formation of the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), of which ATI was a founding member, together with NEC and 6 different graphics adapter producers.
In 1987 ATI added the Graphics Solution Plus collection to its product line for OEM’s, which used IBM’s PC/XT ISA 8-bit bus for Intel 8086/8088 based mostly IBM PC’s. The chip supported MDA, CGA and EGA graphics modes through dip switches. It was mainly a clone of the Plantronics Colorplus board, however with room for 64kb of reminiscence. Paradise Systems’ PEGA1, 1a, and 2a (256kB) launched in 1987 have been Plantronics clones as nicely.
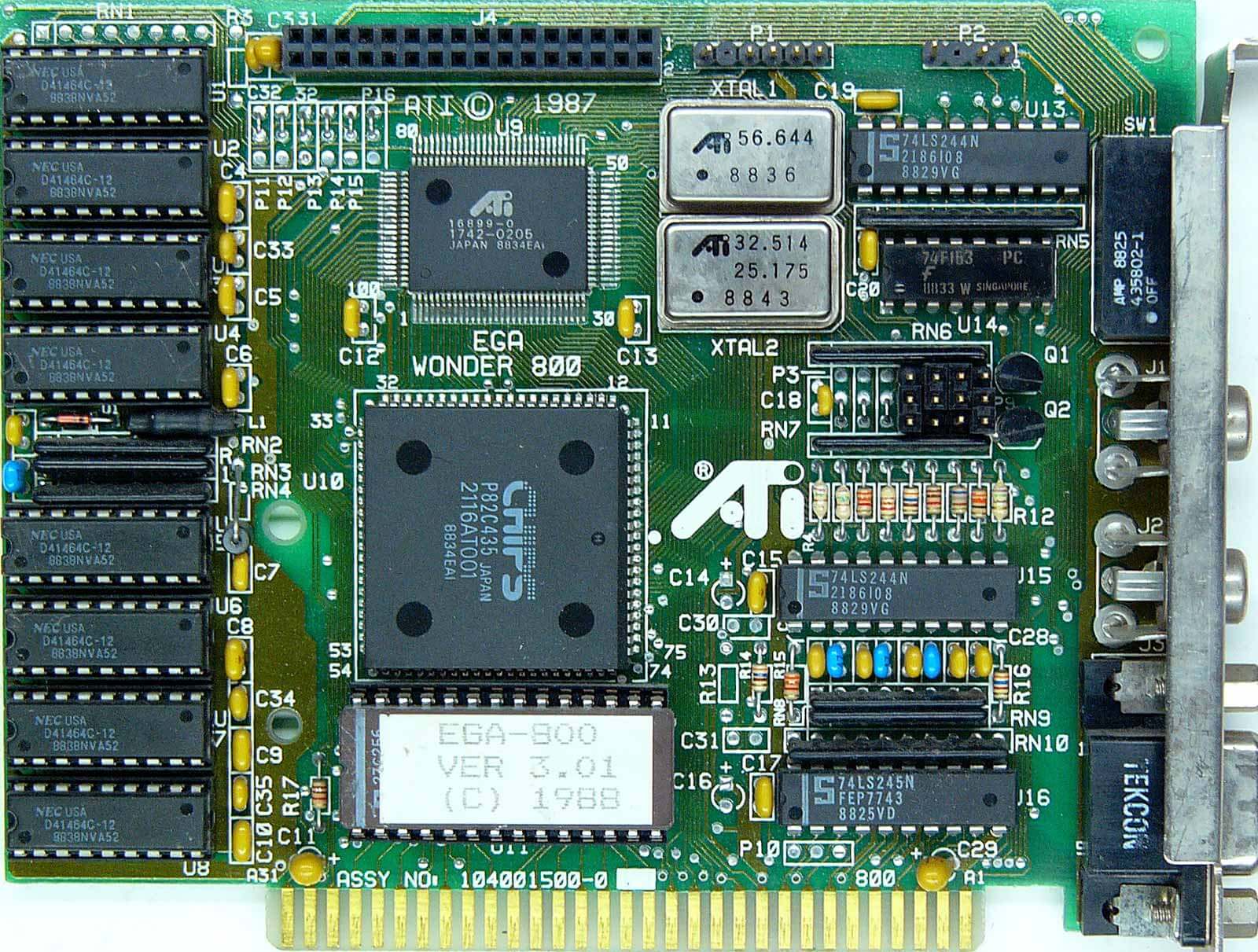
The EGA Wonder collection 1 to 4 arrived in March for $399, that includes 256KB of DRAM in addition to compatibility with CGA, EGA and MDA emulation with as much as 640×350 and 16 colours. Extended EGA was accessible for the collection 2,3 and 4.
Filling out the excessive finish was the EGA Wonder 800 with 16-color VGA emulation and 800×600 decision help, and the VGA Improved Performance (VIP) card, which was mainly an EGA Wonder with a digital-to-analog (DAC) added to offer restricted VGA compatibility. The latter value $449 plus $99 for the Compaq enlargement module.
ATI was removed from being alone using the wave of shopper urge for food for private computing.
Many new corporations and merchandise arrived that yr.. Among them have been Trident, SiS, Tamerack, Realtek, Oak Technology, LSI’s G-2 Inc., Hualon, Cornerstone Imaging and Winbond — all fashioned in 1986-87. Meanwhile, corporations akin to AMD, Western Digital/Paradise Systems, Intergraph, Cirrus Logic, Texas Instruments, Gemini and Genoa, would produce their first graphics merchandise throughout this timeframe.
ATI’s Wonder collection continued to achieve prodigious updates over the following few years.
In 1988, the Small Wonder Graphics Solution with sport controller port and composite out choices grew to become accessible (for CGA and MDA emulation), in addition to the EGA Wonder 480 and 800+ with Extended EGA and 16-bit VGA help, and likewise the VGA Wonder and Wonder 16 with added VGA and SVGA help.
A Wonder 16 was outfitted with 256KB of reminiscence retailed for $499, whereas a 512KB variant value $699.
An up to date VGA Wonder/Wonder 16 collection arrived in 1989, together with the decreased value VGA Edge 16 (Wonder 1024 collection). New options included a bus-Mouse port and help for the VESA Feature Connector. This was a gold-fingered connector much like a shortened knowledge bus slot connector, and it linked through a ribbon cable to a different video controller to bypass a congested knowledge bus.
The Wonder collection updates continued to maneuver apace in 1991. The Wonder XL card added VESA 32K colour compatibility and a Sierra RAMDAC, which boosted most show decision to 640×480 @ 72Hz or 800×600 @ 60Hz. Prices ranged by way of $249 (256KB), $349 (512KB), and $399 for the 1MB RAM choice. A decreased value model referred to as the VGA Charger, based mostly on the earlier yr’s Basic-16, was additionally made accessible.
The Mach collection launched with the Mach8 in May of that yr. It offered as both a chip or board that allowed, through a programming interface (AI), the offloading of restricted 2D drawing operations akin to line-draw, color-fill and bitmap mixture (Bit BLIT).ATI added a variation of the Wonder XL that integrated a Creative Sound Blaster 1.5 chip on an prolonged PCB. Known because the VGA Stereo-F/X, it was able to simulating stereo from Sound Blaster mono information at one thing approximating FM radio high quality.
Graphics boards such because the ATI VGAWonder GT, provided a 2D + 3D choice, combining the Mach8 with the graphics core (28800-2) of the VGA Wonder+ for its 3D duties. The Wonder and Mach8 pushed ATI by way of the CAD$100 million gross sales milestone for the yr, largely on the again of Windows 3.0’s adoption and the elevated 2D workloads that might be employed with it.
S3 Graphics was fashioned in early 1989 and produced its first 2D accelerator chip and a graphics card eighteen months later, the S3 911 (or 86C911). Key specs for the latter included 1MB of VRAM and 16-bit colour help.
The S3 911 was outmoded by the 924 that very same yr — it was mainly a revised 911 with 24-bit colour — and once more up to date the next yr with the 928 which added 32-bit colour, and the 801 and 805 accelerators. The 801 used an ISA interface, whereas the 805 used VLB. Between the 911’s introduction and the appearance of the 3D accelerator, the market was flooded with 2D GUI designs based mostly on S3’s authentic — notably from Tseng labs, Cirrus Logic, Trident, IIT, ATI’s Mach32 and Matrox’s MAGIC RGB.
In January 1992, Silicon Graphics Inc (SGI) launched OpenGL 1.0, a multi-platform vendor agnostic utility programming interface (API) for each 2D and 3D graphics.
Microsoft was creating a rival API of their very own referred to as Direct3D and did not precisely break a sweat ensuring OpenGL ran in addition to it might below Windows.
OpenGL advanced from SGI’s proprietary API, referred to as the IRIS GL (Integrated Raster Imaging System Graphical Library). It was an initiative to maintain non-graphical performance from IRIS, and permit the API to run on non-SGI programs, as rival distributors have been beginning to loom on the horizon with their very own proprietary APIs.
Initially, OpenGL was aimed on the skilled UNIX based mostly markets, however with developer-friendly help for extension implementation it was shortly adopted for 3D gaming.
Microsoft was creating a rival API of their very own referred to as Direct3D and did not precisely break a sweat ensuring OpenGL ran in addition to it might below the brand new Windows working programs.
Things got here to a head a couple of years later when John Carmack of id Software, whose beforehand launched Doom had revolutionised PC gaming, ported Quake to make use of OpenGL on Windows and overtly criticised Direct3D.
Microsoft’s intransigence elevated as they denied licensing of OpenGL’s Mini-Client Driver (MCD) on Windows 95, which might permit distributors to decide on which options would have entry to {hardware} acceleration. SGI replied by creating the Installable Client Driver (ICD), which not solely supplied the identical capability, however did so even higher since MCD coated rasterization solely and ICD added lighting and rework performance (T&L).
During the rise of OpenGL, which initially gained traction within the workstation area, Microsoft was busy eyeing the rising gaming market with designs on their very own proprietary API. They acquired RenderMorphics in February 1995, whose Reality Lab API was gaining traction with builders and have become the core for Direct3D.
At about the identical time, 3dfx’s Brian Hook was writing the Glide API that was to change into the dominant API for gaming. This was partly attributable to Microsoft’s involvement with the Talisman undertaking (a tile based mostly rendering ecosystem), which diluted the assets meant for DirectX.
As D3D grew to become broadly accessible on the again of Windows adoption, proprietary APIs akin to S3d (S3), Matrox Simple Interface, Creative Graphics Library, C Interface (ATI), SGL (PowerVR), NVLIB (Nvidia), RRedline (Rendition) and Glide, started to lose favor with builders.
It did not assist issues that a few of these proprietary APIs have been allied with board producers below growing stress so as to add to a quickly increasing function checklist. This included increased display resolutions, elevated colour depth (from 16-bit to 24 after which 32), and picture high quality enhancements akin to anti-aliasing. All of those options referred to as for elevated bandwidth, graphics effectivity and quicker product cycles.
By 1993, market volatility had already compelled numerous graphics corporations to withdraw from the enterprise, or to be absorbed by opponents.
The yr 1993 ushered in a flurry of recent graphics opponents, most notably Nvidia, based in January of that yr by Jen-Hsun Huang, Curtis Priem and Chris Malachowsky. Huang was beforehand the Director of Coreware at LSI whereas Priem and Malachowsky each got here from Sun Microsystems the place they’d beforehand developed the SunSPARC-based GX graphics structure.
Fellow newcomers Dynamic Pictures, ARK Logic, and Rendition joined Nvidia shortly thereafter.
Market volatility had already compelled numerous graphics corporations to withdraw from the enterprise, or to be absorbed by opponents. Amongst them have been Tamerack, Gemini Technology, Genoa Systems, Hualon, Headland Technology (purchased by SPEA), Acer, Motorola and Acumos (purchased by Cirrus Logic).
One firm that was shifting from energy to energy nevertheless was ATI.
As a forerunner of the All-In-Wonder collection, late November noticed the announcement of ATI’s 68890 PC TV decoder chip which debuted contained in the Video-It! card. The chip was in a position to seize video at 320×240 @ 15 fps, or 160×120 @ 30 fps, in addition to compress/decompress in actual time because of the onboard Intel i750PD VCP (Video Compression Processor). It was additionally in a position to talk with the graphics board through the information bus, thus negating the necessity for dongles or ports and ribbon cables.
The Video-It! retailed for $399, whereas a lesser featured mannequin named Video-Basic accomplished the line-up.
Five months later, in March, ATI belatedly launched a 64-bit accelerator; the Mach64.
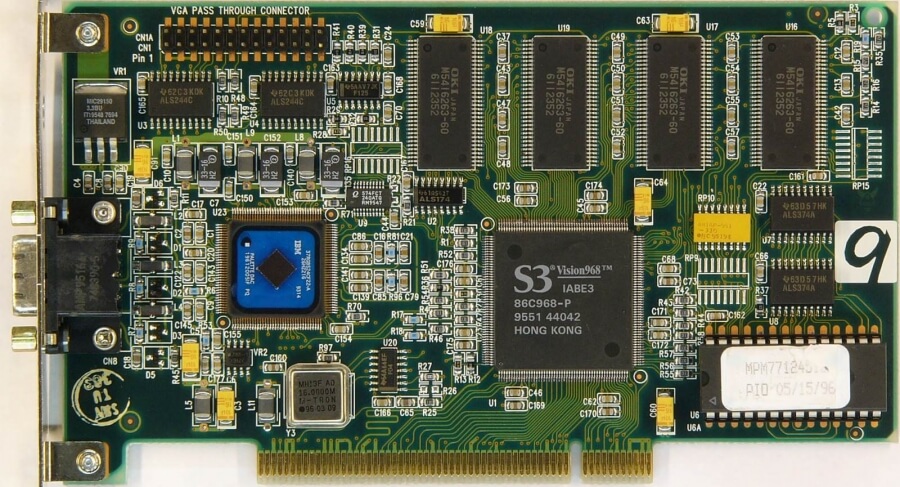
The monetary yr had not been type to ATI with a CAD$2.7 million loss because it slipped within the market amid robust competitors. Rival boards included the S3 Vision 968, which was picked up by many board distributors, and the Trio64 which picked up OEM contracts from Dell (Dimension XPS), Compaq (Presario 7170/7180), AT&T (Globalyst),HP (Vectra VE 4), and DEC (Venturis/Celebris).

Released in 1995, the Mach64 notched numerous notable firsts. It grew to become the primary graphics adapter to be accessible for PC and Mac computer systems within the type of the Xclaim ($450 and $650 relying on onboard reminiscence), and, together with S3’s Trio, provided full-motion video playback acceleration.
The Mach64 additionally ushered in ATI’s first professional graphics playing cards, the 3D Pro Turbo and 3D Pro Turbo+PC2TV, priced at a cool $599 for the 2MB choice and $899 for the 4MB.
The following month noticed a know-how start-up referred to as 3DLabs rise onto the scene, born when DuPont’s Pixel graphics division purchased the subsidiary from its father or mother firm, together with the GLINT 300SX processor able to OpenGL rendering, fragment processing and rasterization. Due to their excessive value the corporate’s playing cards have been initially aimed on the skilled market. The Fujitsu Sapphire2SX 4MB retailed for $1,600-$2,000, whereas an 8MB ELSA GLoria 8 was $2,600-$2,850. The 300SX, nevertheless, was meant for the gaming market.
S3 appeared to be in every single place at the moment. The high-end OEM marked was dominated by the corporate’s Trio64 chipsets that built-in DAC, a graphics controller, and clock synthesiser right into a single chip.
The Gaming GLINT 300SX of 1995 featured a much-reduced 2MB of reminiscence. It used 1MB for textures and Z-buffer and the opposite for body buffer, however got here with an choice to extend the VRAM for Direct3D compatibility for an additional $50 over the $349 base value. The card didn’t make headway in an already crowded market, however 3DLabs was already engaged on a successor within the Permedia collection.
S3 appeared to be in every single place at the moment. The high-end OEM marked was dominated by the corporate’s Trio64 chipsets that built-in DAC, a graphics controller, and clock synthesiser right into a single chip. They additionally utilized a unified body buffer and supported {hardware} video overlay (a devoted portion of graphics reminiscence for rendering video as the appliance requires). The Trio64 and its 32-bit reminiscence bus sibling, the Trio32, have been accessible as OEM items and standalone playing cards from distributors akin to Diamond, ELSA, Sparkle, STB, Orchid, Hercules and Number Nine. Diamond Multimedia’s costs ranged from $169 for a ViRGE based mostly card, to $569 for a Trio64+ based mostly Diamond Stealth64 Video with 4MB of VRAM.
The mainstream finish of the market additionally included choices from Trident, a very long time OEM provider of no-frills 2D graphics adapters who had lately added the 9680 chip to its line-up. The chip boasted many of the options of the Trio64 and the boards have been usually priced across the $170-200 mark. They provided acceptable 3D efficiency in that bracket, with good video playback functionality.
Other newcomers within the mainstream market included Weitek’s Power Player 9130, and Alliance Semiconductor’s ProMovement 6410 (normally seen because the Alaris Matinee or FIS’s OptiViewPro). Both provided wonderful scaling with CPU velocity, whereas the latter mixed the robust scaling engine with antiblocking circuitry to acquire easy video playback, which was significantly better than in earlier chips such because the ATI Mach64, Matrox MGA 2064W and S3 Vision968.

Nvidia launched their first graphics chip, the NV1, in May, and have become the primary business graphics processor able to 3D rendering, video acceleration, and built-in GUI acceleration.
They partnered with ST Microelectronic to provide the chip on their 500nm course of and the latter additionally promoted the STG2000 model of the chip. Although it was not an enormous success, it did signify the primary monetary return for the corporate. Unfortunately for Nvidia, simply as the primary vendor boards began transport (notably the Diamond Edge 3D) in September, Microsoft finalized and launched DirectX 1.0.
The D3D graphics API confirmed that it relied upon rendering triangular polygons, the place the NV1 used quad texture mapping. Limited D3D compatibility was added through driver to wrap triangles as quadratic surfaces, however an absence of video games tailor-made for the NV1doomed the cardboard as a jack of all trades, grasp of none.
Most of the video games have been ported from the Sega Saturn. A 4MB NV1 with built-in Saturn ports (two per enlargement bracket linked to the cardboard through ribbon cable), retailed for round $450 in September 1995.
Microsoft’s late adjustments and launch of the DirectX SDK left board producers unable to immediately entry {hardware} for digital video playback. This meant that just about all discrete graphics playing cards had performance points in Windows 95. Drivers below Win 3.1 from quite a lot of corporations have been usually faultless in contrast.

The first public demonstration of it got here on the E3 online game convention held in Los Angeles in May the next yr. The card itself grew to become accessible a month later. The 3D Rage merged the 2D core of the Mach64 with 3D functionality.ATI introduced their first 3D accelerator chip, the 3D Rage (also referred to as the Mach 64 GT), in November 1995.
Late revisions to the DirectX specification meant that the 3D Rage had compatibility issues with many video games that used the API — primarily the shortage of depth buffering. With an on-board 2MB EDO RAM body buffer, 3D modality was restricted to 640x480x16-bit or 400x300x32-bit. Attempting 32-bit colour at 600×480 usually resulted in onscreen colour corruption, and 2D decision peaked at 1280×1024. If gaming efficiency was mediocre, the complete display MPEG playback capability not less than went a way in balancing the function set.
The efficiency race was over earlier than it had began, with the 3Dfx Voodoo Graphics successfully annihilating all competitors.
ATI reworked the chip, and in September the Rage II launched. It rectified the D3DX problems with the primary chip along with including MPEG2 playback help. Initial playing cards, nevertheless, nonetheless shipped with 2MB of reminiscence, hampering efficiency and having points with perspective/geometry rework, As the collection was expanded to incorporate the Rage II+DVD and 3D Xpression+, reminiscence capability choices grew to 8MB.
While ATI was first to market with a 3D graphics resolution, it did not take too lengthy for different opponents with differing concepts of 3D implementation to reach on the scene. Namely, 3dfx, Rendition, and VideoLogic.
In the race to launch new merchandise into {the marketplace}, 3Dfx Interactive received over Rendition and VideoLogic. The efficiency race, nevertheless, was over earlier than it had began, with the 3Dfx Voodoo Graphics successfully annihilating all competitors.
This is the primary article on our History of the GPU collection. If you loved this, hold studying as we take a stroll down reminiscence lane to the heyday of 3Dfx, Rendition, Matrox, and a younger firm referred to as Nvidia.



