
Ouch! The financial institution that funded many Silicon Valley startups has run out of cash within the second-largest financial institution failure in U.S. historical past. Failure would severely harm the enterprise capital financial system and is already hurting the banking sector, at the very least within the quick time period. However, the danger of a 2008-style crash is low.
Silicon Valley Bank collapsed on Friday after an enormous run on deposits that put practically $175 billion (together with cash from among the largest tech firms) beneath the management of the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation). The financial institution has been an essential supply of enterprise capital funding for expertise firms, based on The New York Times.
The company is exploring a possible sale because it halted all buying and selling in its shares. The FDIC will maintain deposits and property of Silicon Valley Bank on the not too long ago accomplished Santa Clara National Bank, which is able to start operations on Monday. Checks issued by Silicon Valley Bank will nonetheless clear.
However, the financial institution’s coverage solely covers deposits as much as $250,000. Accounts above that quantity will ultimately obtain certificates partially repaying uninsured funds. Silicon Valley Bank has lower than 3% of its deposits insured as a result of it offers with many massive tech firms.
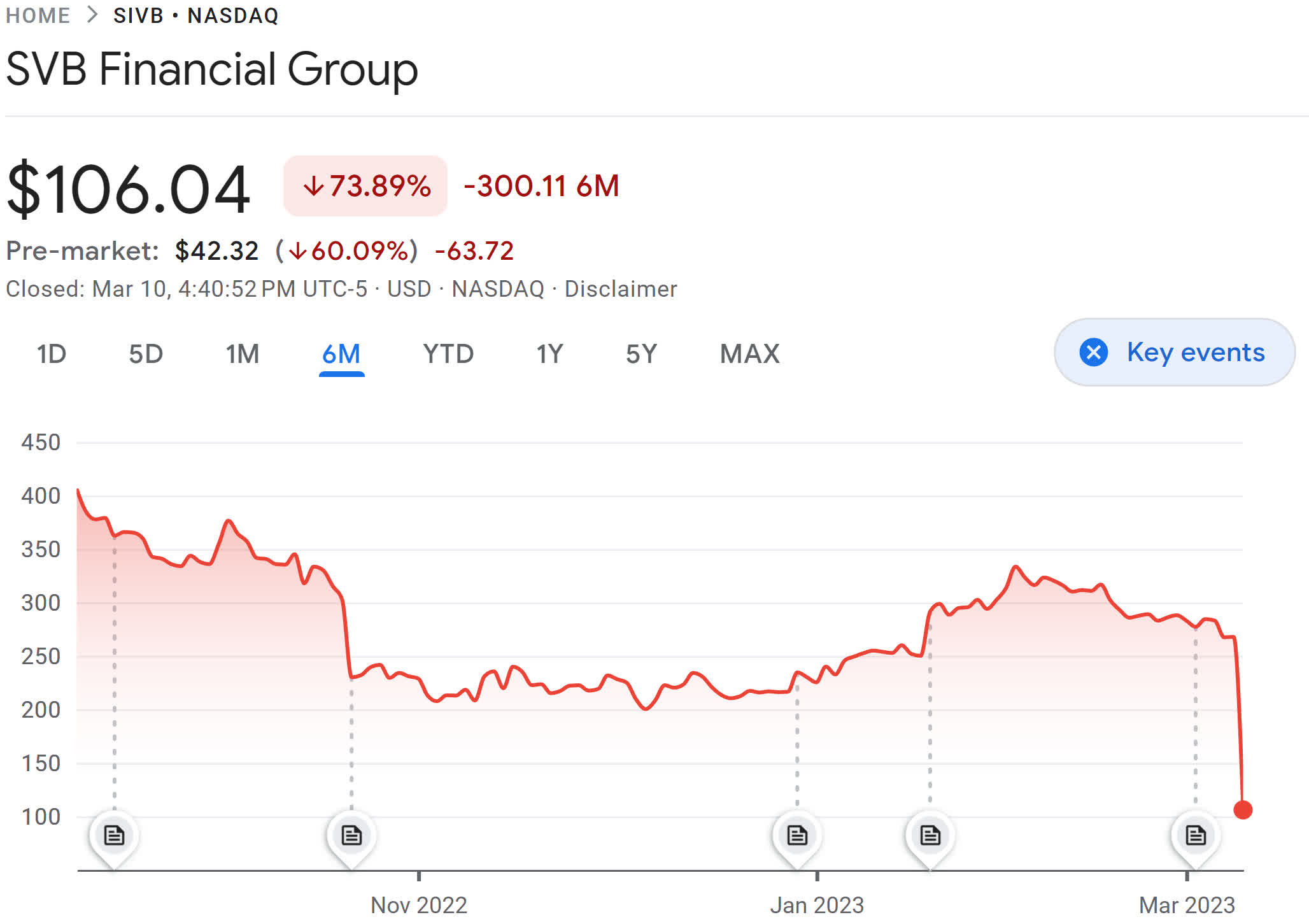
Silicon Valley Bank makes use of its wealthy cash from enterprise funds to put money into bonds, which produced Solid returns with low rates of interest. Between 2018 and 2021, the financial institution’s deposits grew from $49 billion to $189.2 billion. However, final yr’s federal fee hike upended that technique.
The financial institution responded this week with some cautious steps, however the announcement of the strikes sparked panic. Silicon Valley Bank offered some securities at a loss, offered $21 billion in investments, borrowed $15 billion, and raised money by means of emergency inventory gross sales. The poor response to the selections sparked a run on the financial institution as its share value plummeted.
The aftermath despatched Signature Bank and Western Alliance down greater than 20% on Friday. PacWest Bancorp fell greater than 35%. However, different massive banks, corresponding to JPMorgan Chase and Wells Fargo, carried out effectively, closing barely increased on Friday. Bank of America and Morgan Stanley fell barely.
The SVB collapse was the most important U.S. financial institution failure because the collapse of Washington Mutual in 2008 — the most important in U.S. historical past — affecting $300 billion in buyer deposits.


