
Why it matters: Nuclear fusion is certainly considered a ultimate goal of clean, green power, perhaps supplying near-limitless energy without having the downsides of fossil fuels or fission that is nuclear. The jury is still out on whether fusion power will ever be viable, but scientists have made a significant step that is early the lengthy roadway to locating completely.
Researchers have actually accomplished initial fusion that is nuclear that produced more energy than it took to start the reaction. The result represents a milestone that is significant atomic fusion power development, but we are most likely however numerous years far from fusion energy flowers.
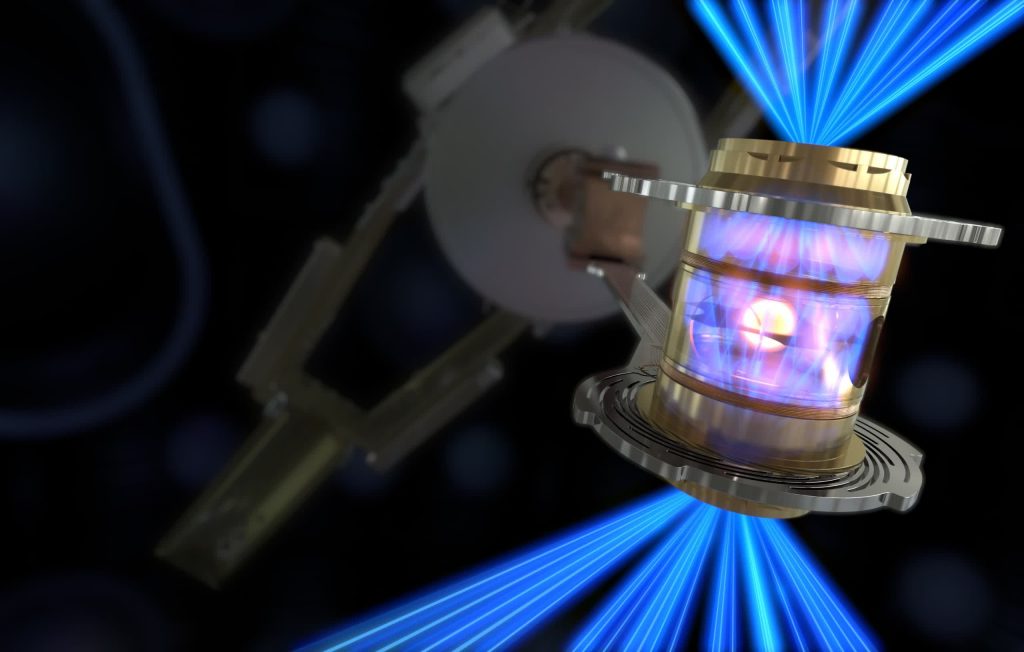
The US Department of Energy and its own National Nuclear Security Administration launched that the* that is( achieved what it calls “fusion ignition” or “scientific energy breakeven.” On December 5, the* that is( (NIF) in Livermore, California, utilized 192 lasers to provide 2.05 megajoules of power up to a little gasoline pellet to trigger a fusion effect creating 3.15 megajoules.
The Experiment didn’t yield a complete lot of energy, and it took hundreds of megajoules to power the lasers. However, it shows that a energy that is net from fusion could possibly be feasible. Future analysis would need experts to style much more lasers that are efficient then figure out how to create sustained fusion through rapid-fire bursts. If they accomplish all that, perhaps they could discover more cost-effective methods for mass production and integration into the energy that is current.
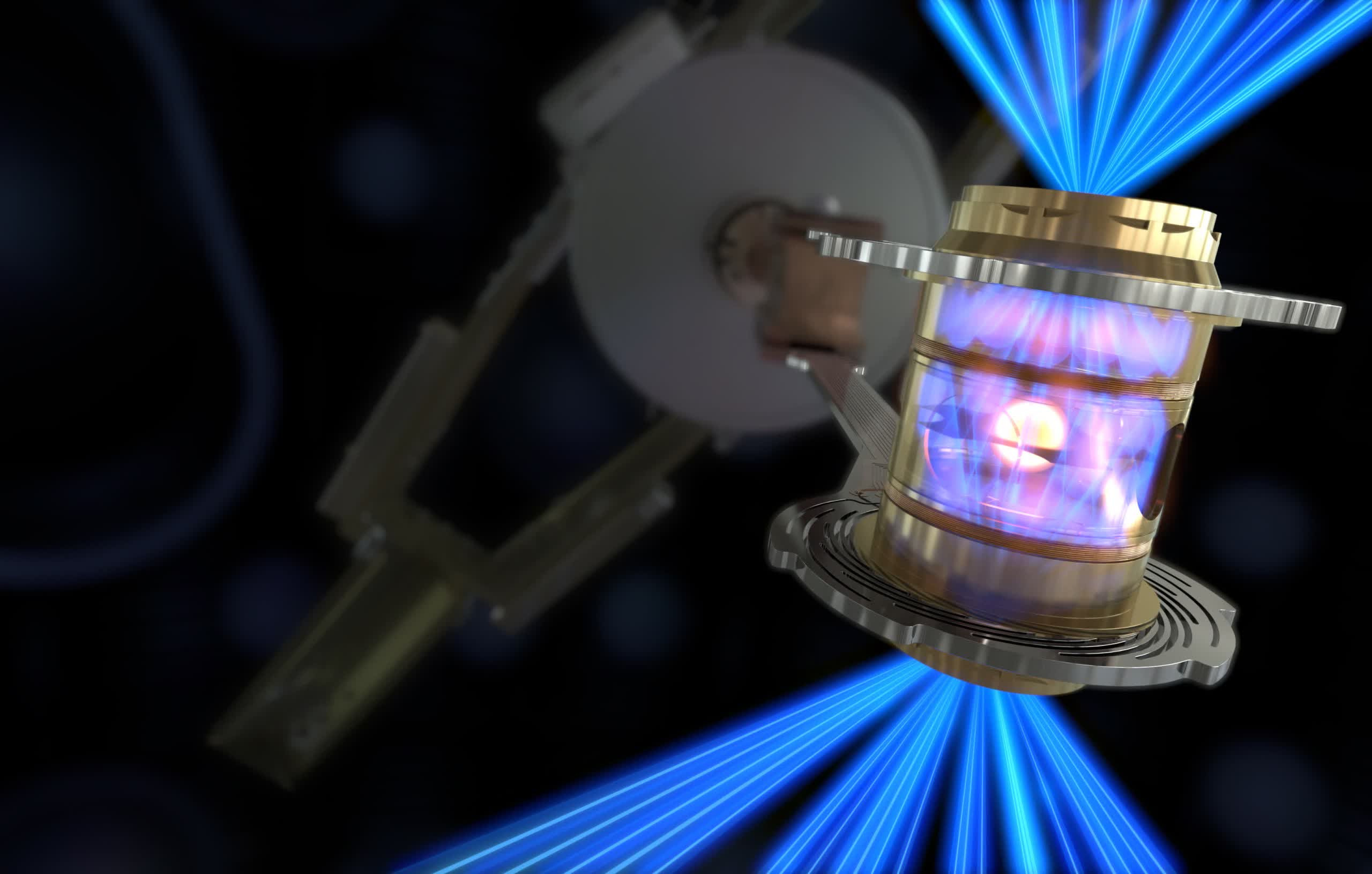
Other services around the world will also be looking into fusion that is nuclear strategies other than lasers. The DIII-D facility in San Diego operates a donut-shaped “Tokamak” chamber to turn fuel into superheated plasma where fusion reactions might happen.
Nuclear fusion is the process that powers the sun and other stars. In a star, it occurs when hydrogen nuclei — stripped of their electrons by the pressure that is massive of celebrity’s interior — collide to produce helium atoms. Helium atoms have little less mass as compared to hydrogen atoms that made all of them, plus the distinction is circulated as power, which fusion rectors desire to harness.
The NIF accomplishes this by firing lasers in a pipe to warm its wall space to an incredible number of levels Celsius, producing X-rays around. A gasoline pellet inside provides the hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tritium, therefore the X-rays push the isotopes to fuse, making helium.
Nuclear fusion can theoretically produce large numbers of power in comparison to existing gasoline resources without creating greenhouse fumes or waste that is dangerous. However, it remains to be seen if the technology will be economically workable ever.


