
[ad_1]
What simply occurred? The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in early 2020 introduced plans to refresh its getting old supercomputer community. On Tuesday, the company inaugurated its two new machines in Manassas, Virginia, and Phoenix, Arizona.
The Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) Cray supercomputers, dubbed Dogwood and Cactus, had been named after flora from their geographic places. Each is outfitted with 2,560 AMD Epyc Rome 64-core 7742 server CPUs for a mixed 327,680 cores that may function at as much as 12.1 petaflops, which is 3 times quicker than NOAA’s earlier setup.
The techniques presently rank because the forty ninth and fiftieth quickest computer systems on the earth and are changing Cray and IBM supercomputers situated in Reston, Virginia, and Orlando, Florida. Coupled with current machines in Tennessee, West Virginia, Mississippi and Colorado, NOAA’s supercomputing capability now sits at 42 petaflops.
For comparability, the quickest supercomputer on the earth is housed on the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee. It is able to a staggering 1.1 exaflops of efficiency with a peak of 1.69 exaflops.
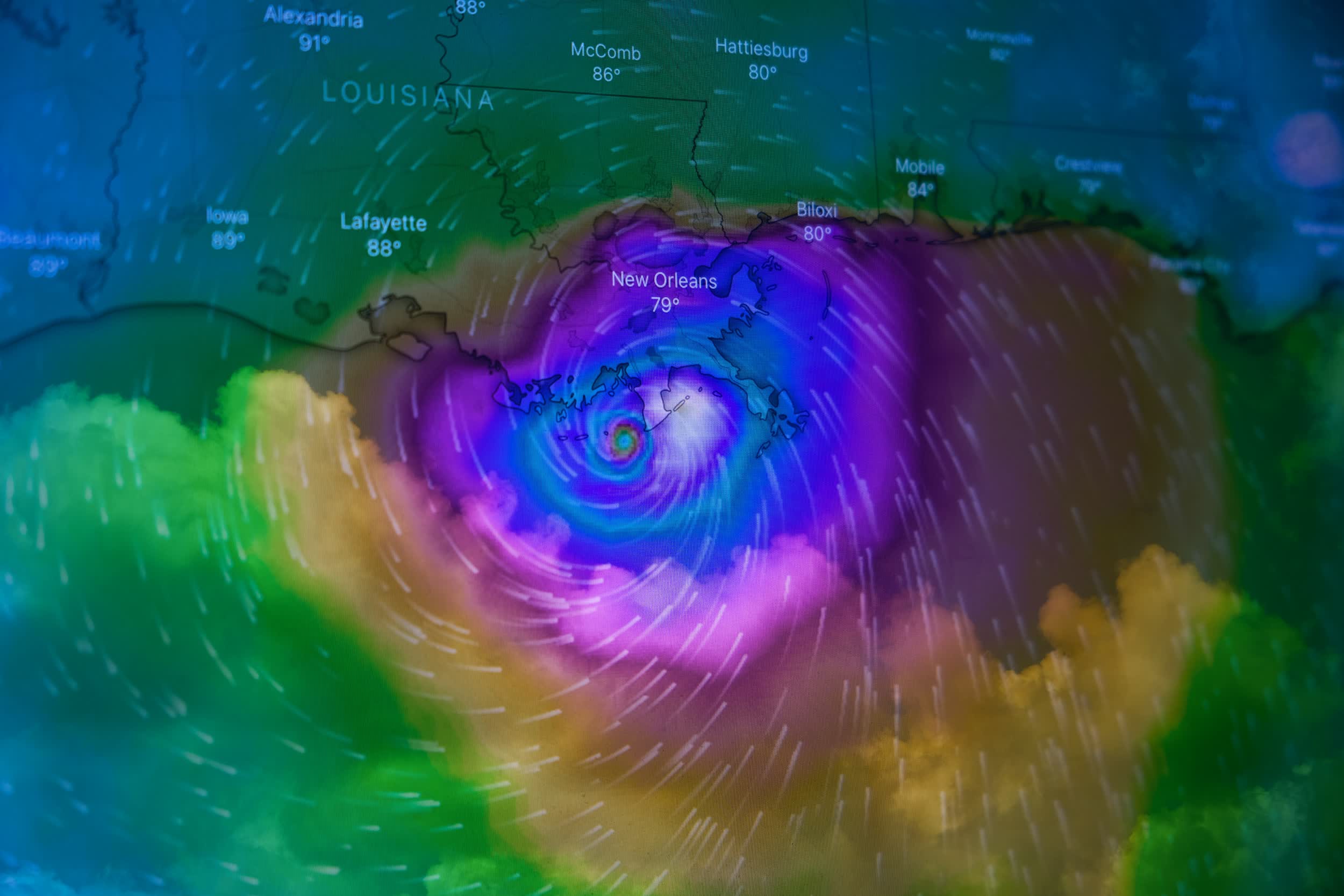
NOAA Administrator Rick Spinrad mentioned extra computing energy will allow them to offer the general public with extra detailed climate forecasts additional upfront. Specifically, NOAA will be capable of create higher-resolution fashions that higher depict small-scale options similar to thunderstorms and produce extra particular person mannequin simulations to quantify mannequin certainty.
This fall, NOAA will improve to the US Global Forecast System (GFS) and prep a brand new hurricane forecast mannequin known as Hurricane Analysis and Forecast System (HAFS) to be used in the course of the 2023 hurricane season.
Image credit score: Brian McGowan
[ad_2]


