PSAs: Hackers can use embedded iframes to steal your web site usernames and passwords. This is a weak point of all password managers, and most work round it in varied methods, together with warning customers after they’re on a login web page with an iframe or do not belief a subdomain. The solely exception is Bitwarden, which decided in 2018 that the risk was not severe sufficient to deal with.
In its assist web page about “autofill,” Bitwarden advises customers to show off their browser’s password autofill options, as they intervene with their password administration options.It additionally mentions that it is a good thought as a result of “consultants usually agree that the built-in [browser] Password managers are extra susceptible than devoted options like Bitwarden,” which is usually true.
Unfortunately, its password filler most likely is not a lot better than your browser’s. Security researchers at Flashpoint have found that Bitwarden’s autofill extension handles web sites with embedded iframes in an insecure method. Understanding this vulnerability requires a fundamental understanding of iframes.
Web web site builders use inline body parts, or iframes, to embed a part of one other internet web page into their websites. For instance, TechSpot makes use of iframes to embed YouTube movies into its articles. It may also be used to embed internet kinds. In normal, iframes are protected to make use of so long as embedded materials from exterior websites is not compromised, and that is the place managers run into issues.
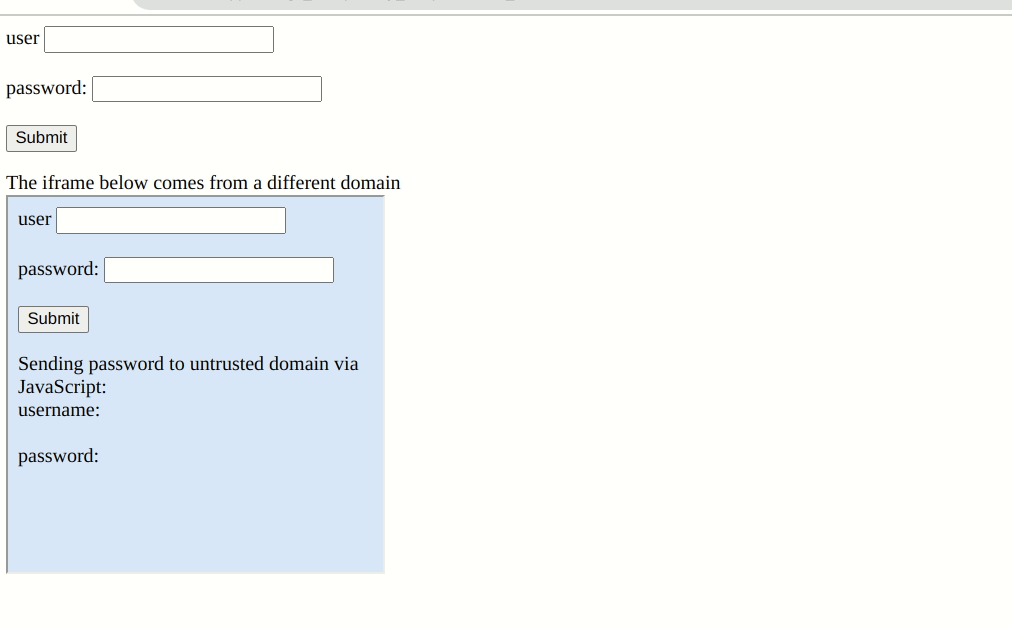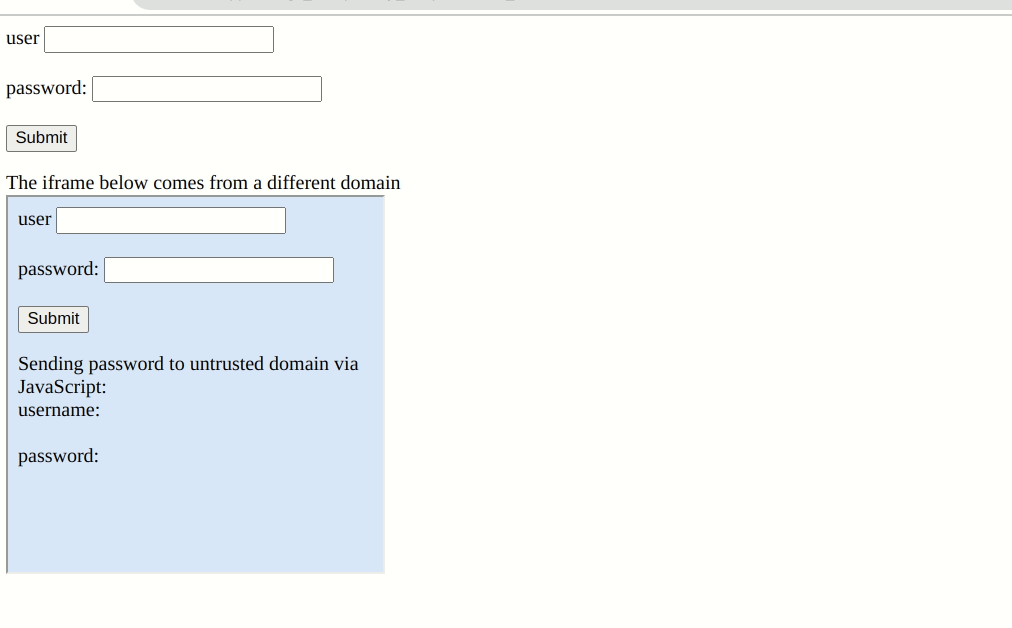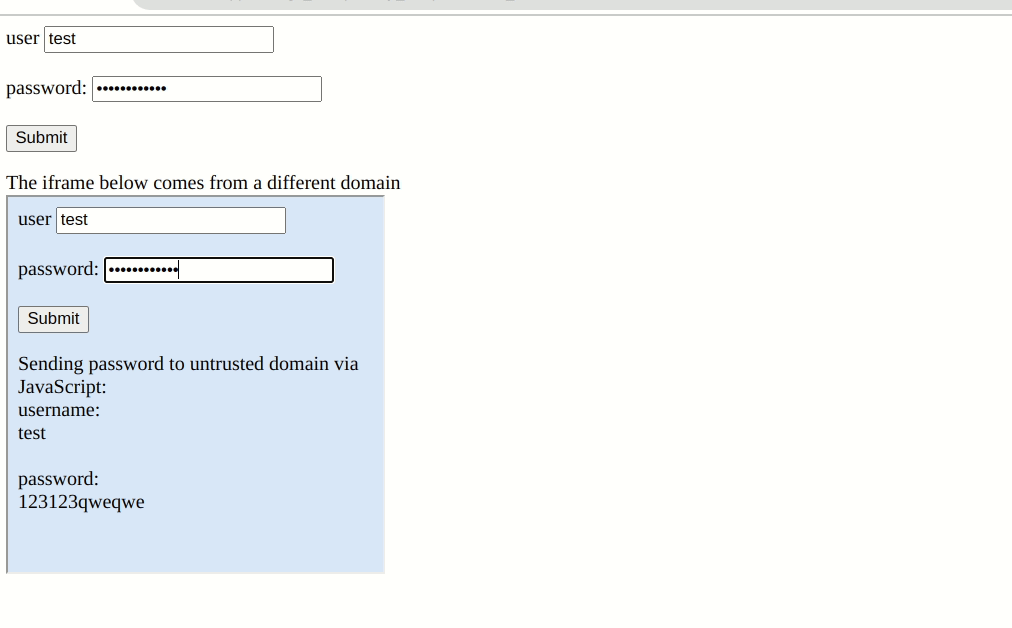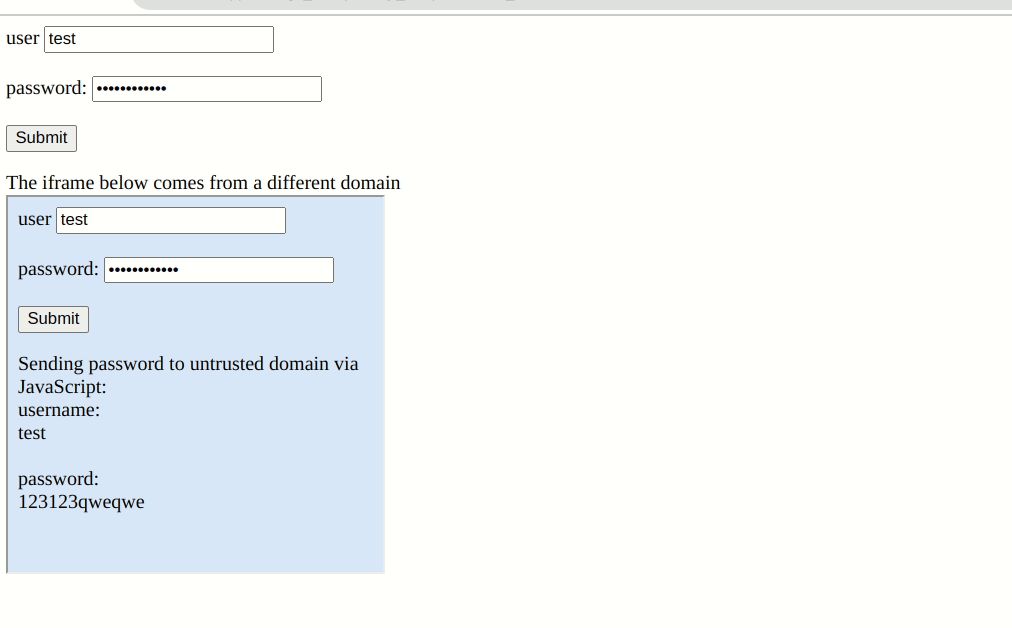
Password Extension Autofill Credentials on any webpage customers have saved their credentials by design. They may even pre-emptively fill out login kinds with out consumer interplay. In Bitwarden’s paper, there’s a setting referred to as “Autofill on web page load”. However, the extension will carry out this performance throughout the iframe with out the “similar origin coverage” examine. So if a web page has a malicious iframe from a special area, the administrator will unknowingly hand over your credentials as a way to ship them to the hacker’s server.
Most password managers have checks in place to no less than warn customers of potential risks. However, Bitwarden doesn’t block or warn that iframes from completely different domains could steal credentials. It assumes that every one iframes on the login web page are safe. It stated as a lot in its 2018 safety report, however extra on that later.
Of course, this will solely occur if a trusted web site has already been compromised, proper? According to Flashpoint, that is not essentially true.
Obviously, if a hacker has gained sufficient of a foothold to embed an iframe on a professional web site, customers may have greater issues than this weak point on their fingers. In this case, no password administration extension can assist. However, some professional web sites use kinds from one other area and embed them in iframes. If hackers can compromise secondary sources, they’ve a proxy for stealing data from trusted web sites.
Flashpoint acknowledges that it is a uncommon prevalence and confirmed it by spot-checking a number of websites that use iframes on their login pages. However, there may be one other downside. Bitwarden’s default URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) matching setting is “Base Domain”. Therefore, the extension gives password autofill each time the top-level and second-level domains match.
The downside is that some internet hosting providers enable customers to host “arbitrary content material” beneath subdomains, which makes it comparatively straightforward to spoof login pages.
“For instance, if an organization has a login web page and permits customers to contribute content material beneath these customers, these customers are in a position to steal credentials from the Bitwarden extension,” Flashpoint stated. “During our analysis, we recognized a number of main web sites that present this actual atmosphere. If a consumer utilizing the Bitwarden browser extension visits a specifically crafted web page hosted on these internet providers, an attacker is ready to steal the credentials saved for the corresponding area “
Curiously, when Flashpoint contacted Bitwarden concerning the vulnerability to coordinate disclosure, the corporate famous that it had recognized about it since 2018.
“Because Bitwarden doesn’t examine the URL of every iframe, it’s attainable for an internet site to embed a malicious iframe that Bitwarden will autofill with ‘top-level’ web site credentials,” reads the corporate’s 2018 safety evaluation report. “Unfortunately, there are professional circumstances the place web sites embrace iframe login kinds from domains which can be completely different from their ‘guardian’ web site area. There are at the moment no plans to take any motion.”
In different phrases, Bitwarden is conscious of the issue, however considers the danger acceptable, so will not do something about it, even when it is so simple as having the extension warn you when there’s an iframe on the web page. Flashpoint discovered this inexplicable, as all of Bitwarden’s opponents had some type of mitigation for this assault.
The researchers created a proof of idea utilizing the flaw as an assault vector and an “efficient exploit” they applied privately on a “distinguished internet hosting atmosphere.” They hope that Bitwarden’s builders will change their minds concerning the problem, as nobody had created such an exploit when the corporate initially assessed the vulnerability in 2018. Until Bitwarden fixes the vulnerability, there are some things you are able to do to mitigate it with out switching password managers.
First, flip off the extension’s “Autofill on web page load” setting. You will at all times must set off autofill manually. However, it offers you some respiration room to examine the login web page with out instantly handing over your credentials to the iframe. This is definitely an excellent advice for any password supervisor extension with preemptive autofill.
Second, use that pause to be sure you’re on a trusted area and that the web page is what it sees. Check the URL to be sure you’re on the proper area or subdomain and nothing suspicious. For instance, one thing like “login.wellsfargo.com” could be professional, whereas “credx257.wellsfargo.com” may not.
These steps nonetheless will not defend you from websites utilizing compromised exterior internet kinds, however Flashpoint notes that these circumstances are uncommon. There’s no cause to surrender utilizing a password supervisor, even Bitwarden. Managers are nice that will help you keep your integrity along with your {qualifications}. It is at all times higher to have tons of hard-to-remember strong passwords distinctive to every web site than to reuse weak passwords.