
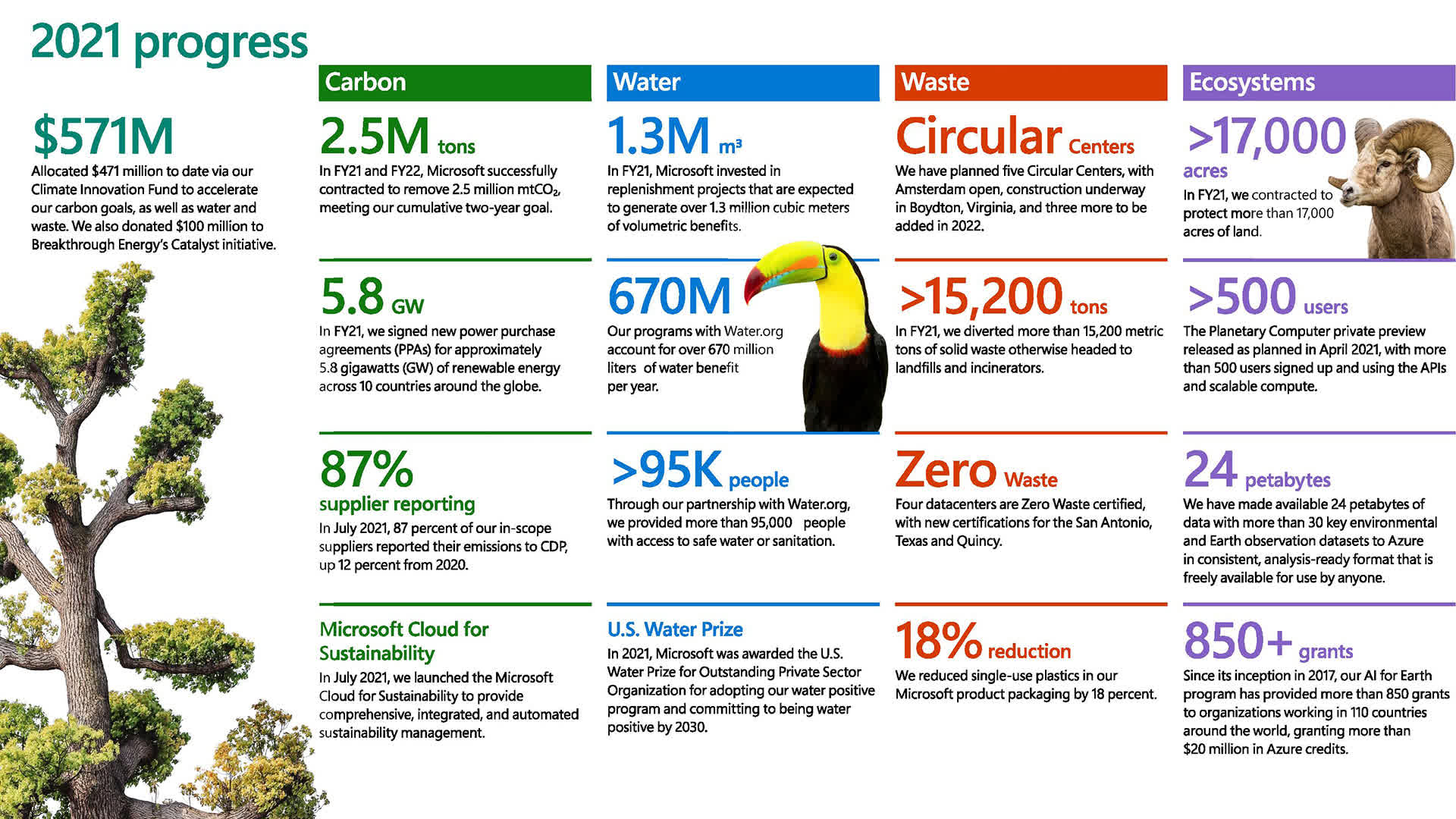
Why it issues: Microsoft builds 50 to 100 new knowledge facilities annually around the globe to assist cloud-based applied sciences and companies. Each middle generates a big and rising carbon footprint, which the software program large has beforehand pledged to remove by 2030. It feels like a tall order, however the tech giants might have a combating likelihood due to some new inexperienced buddies.
Back in 2020, Microsoft introduced its dedication to attain a “carbon damaging” working state by 2030. The firm gave the world an replace on their carbon elimination efforts in 2021, having funded the elimination of greater than 1 billion tonnes of CO2 from the atmosphere. Despite the cancellation, the corporate discovered that a few of their emissions targets, specifically scope 3 emissions, have been nonetheless on the rise.
Scope 3 emissions are emissions for which an organization is not directly accountable however in a roundabout way generated, and are extraordinarily troublesome to regulate. Microsoft has enlisted the assistance of Running Tide, an ocean well being restoration firm specializing in carbon cycle transformations, to assist offset the affect of those emissions and transfer nearer to its carbon damaging objectives.
Running Tide’s resolution relies on diverting carbon from the so-called speedy carbon cycle arrive Slow carbon cycle. The speedy cycle that retains carbon circulating between our oceans and environment completes inside just a few years, maintaining the degrees of carbon circulating in our environment excessive. The sluggish cycle can take tons of of thousands and thousands to thousands and thousands of years to finish, maintaining carbon trapped within the cycle and out of our environment for longer.
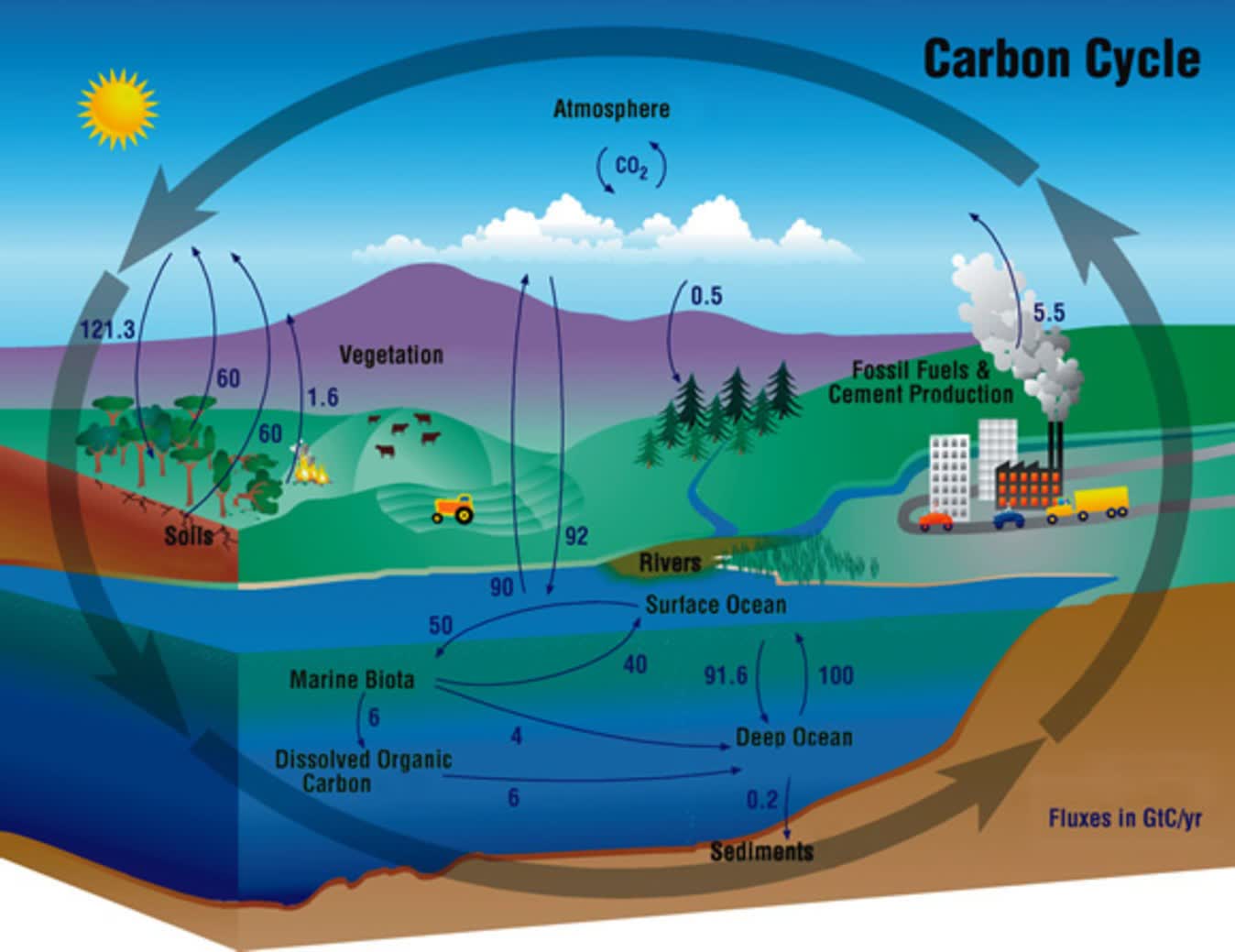
Running Tide seeks to shift the carbon cycle by deploying specialised carbon buoys fabricated from limestone and forest materials tons of of miles from shore. These algae buoys are then allowed to dissolve, serving to to take care of the ocean’s alkalinity because the buoys break down. The seeded algae start to develop, eradicating carbon dioxide from the environment by photosynthesis.
The buoy ultimately degenerates sufficient to lose buoyancy and sink to the underside of the ocean. Once deep sufficient, the carbon is held up by the ocean’s huge water strain, buried underneath ocean sediments, or consumed by aquatic life. According to Running Tide, this conversion exercise and the extraordinary strain of the ocean above retains the carbon trapped out of atmospheric circulation for tons of, typically thousands and thousands of years.
The proposed resolution sounds good in principle, however the know-how is younger and is at present present process additional testing.In an interview with TechCrunch, Running Tide’s Jordan Brener The firm has solely eliminated lower than 1,000 tons of carbon in testing and analysis deployments, and the bigger objective is to take away greater than 12,000 tons of carbon on behalf of Microsoft throughout the subsequent two years.


